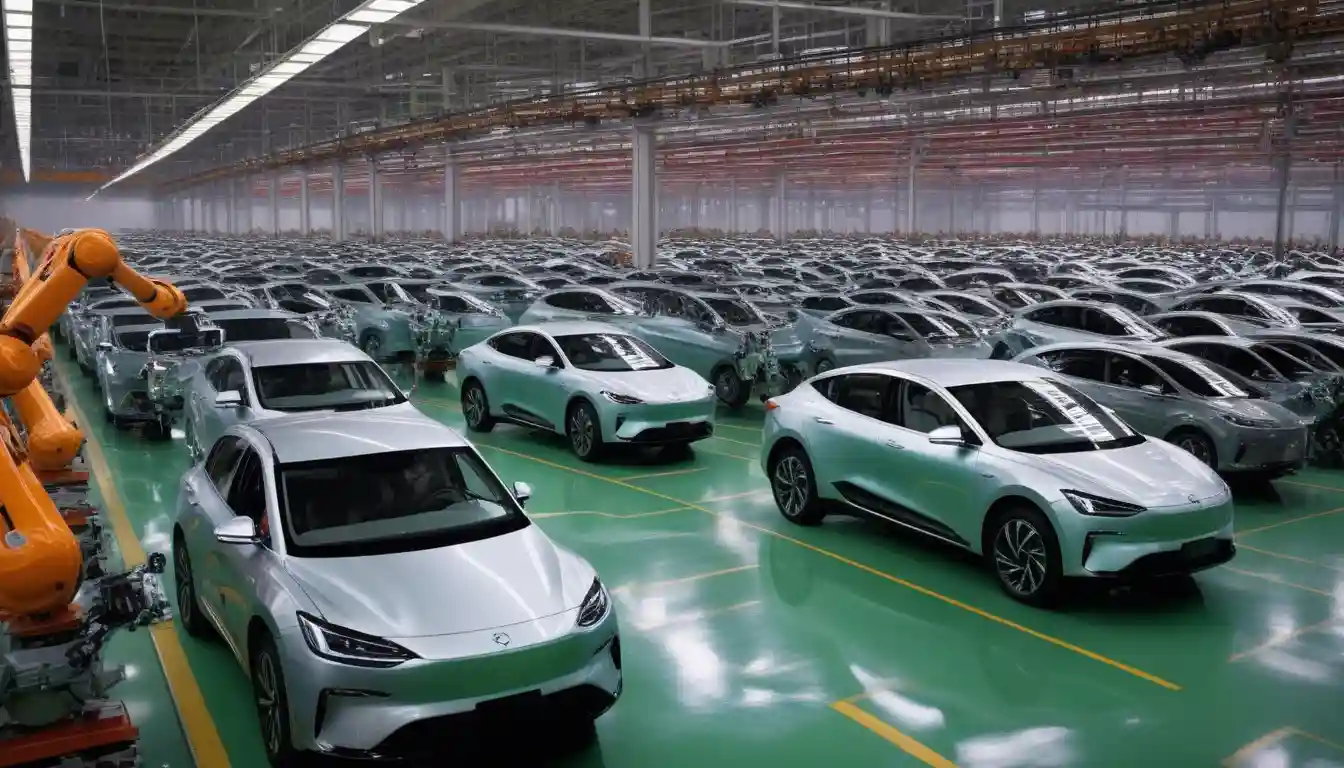

Xiaomi's Beijing Factory Produces Electric Cars Every 76 Seconds Using 700 Robots
The 76-Second Revolution: How Xiaomi's Robotic Assembly Line Redefines the Global EV Race
Beijing — In the sprawling industrial corridors of Beijing's E-Town district, a mechanical symphony plays out every 76 seconds. As another electric vehicle rolls off Xiaomi's production line, more than 700 robots orchestrate a ballet of precision that represents far more than manufacturing efficiency—it embodies China's audacious bid to dominate the global automotive future.
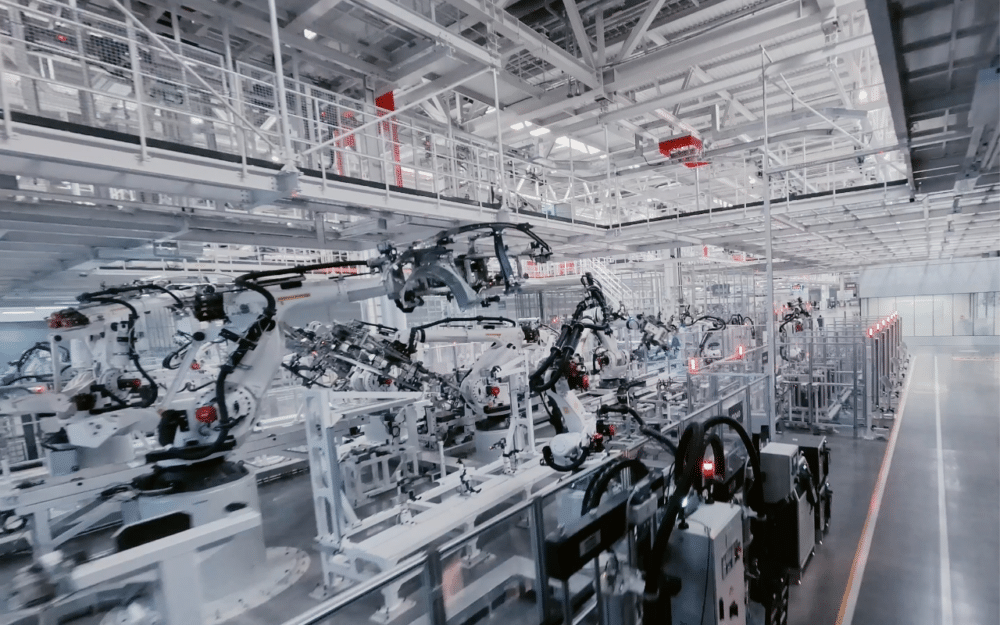
The numbers behind Xiaomi's achievement are staggering: one complete vehicle every 76 seconds translates to approximately 47 cars per hour, potentially yielding over 400,000 vehicles annually from a single facility. This production velocity, achieved through what the company describes as "100 percent automation in key production processes," signals a fundamental shift in how electric vehicles will be manufactured at scale.
Yet beneath these impressive metrics lies a more complex narrative about technological sovereignty, economic transformation, and the emerging battle lines of 21st-century industrial competition.
The Architecture of Acceleration
The Beijing facility represents more than operational excellence—it embodies China's strategic doctrine of "new quality productive forces," a policy framework that prioritizes automation-heavy, technology-driven manufacturing as a pathway to economic supremacy. This approach diverges markedly from traditional automotive manufacturing, where human labor has historically played central roles in assembly and quality control.
Did you know that China’s concept of "new quality productive forces" represents a strategic shift toward innovation-driven, high-tech, and high-efficiency economic growth? It emphasizes breakthroughs in cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence, advanced manufacturing, and biotechnology, aiming to transform traditional industries and build future-oriented sectors. This approach underpins China’s goal of sustainable, high-quality development by focusing on technological self-reliance, upgrading industrial chains, and boosting productivity through innovation—marking a key element of its long-term economic modernization and global competitiveness.
Xiaomi's transition from consumer electronics to automotive manufacturing leverages the company's existing expertise in supply chain optimization and smart manufacturing. The integration of gigacasting technology—consolidating 72 individual parts into single components while eliminating 840 welding operations—demonstrates how cross-industry innovation can compress traditional manufacturing timelines.

Industry observers note that this manufacturing philosophy reflects broader trends reshaping global production. Where traditional automakers have gradually incorporated automation, Xiaomi has designed its entire production ecosystem around robotic precision from inception.
Economic Implications Beyond the Factory Floor
The economic ramifications of ultra-automated EV production extend far beyond Beijing's city limits. Current lithium iron phosphate battery costs have declined to approximately $50-75 per kilowatt-hour in China, creating favorable conditions for aggressive pricing strategies. Xiaomi's SU7 model lineup, priced between RMB 215,900 and 299,900, positions the company to compete directly with established manufacturers while maintaining pathway to profitability. The declining cost of lithium-ion battery packs, showing the dramatic price drop per kWh over the last decade.
| Year | Global Average Price per kWh (in USD) |
|---|---|
| 2014 | $290 |
| 2018 | $128 |
| 2023 | $103 |
| 2024 (YTD) | $78 |
Market analysts suggest that Xiaomi's production capabilities could generate annual revenues exceeding $10 billion if the facility operates at designed capacity. However, the company's management has indicated expectations for automotive unit profitability only in the second half of 2025, reflecting the substantial capital investment required for such advanced manufacturing infrastructure.
The facility's design capacity of 300,000 vehicles annually across two phases positions Xiaomi to capture significant market share in China's domestic EV market, which despite recent growth deceleration, remains the world's largest electric vehicle market.
Geopolitical Manufacturing in the New Cold War
Xiaomi's manufacturing achievements occur against a backdrop of intensifying trade tensions and technological competition. The European Union's implementation of countervailing duties on Chinese electric vehicles, combined with the United States' 100 percent tariff on Chinese EV imports, creates significant barriers to traditional export strategies.
(Table summarizing the tariffs imposed on Chinese-made electric vehicles by the United States and the European Union as of August 2025, showing the varying rates depending on the region and manufacturer)
| Region | Manufacturer/Category | Tariff Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| United States | All Chinese-made EVs | 102.5 |
| European Union | Tesla (China-made) | 17.8 |
| European Union | BYD | 27.0 |
| European Union | Geely | 28.8 |
| European Union | SAIC | 45.3 |
| European Union | Other non-cooperative makers | 45.3 |
These trade restrictions force Chinese manufacturers like Xiaomi to reconsider globalization strategies, potentially accelerating trends toward regional manufacturing and localized supply chains. Some analysts interpret China's emphasis on advanced domestic manufacturing as preparation for a more fragmented global trading environment.
The facility's showcase status in Chinese state media suggests broader symbolic importance beyond commercial objectives. Government officials frequently reference such facilities as evidence of China's technological advancement and industrial modernization, positioning automated manufacturing as central to national competitiveness.
The Human Cost of Mechanical Precision
While Xiaomi's automated production line eliminates many traditional manufacturing jobs, it simultaneously creates demand for specialized technical roles in robotics maintenance, artificial intelligence systems management, and advanced manufacturing engineering. This transition reflects broader labor market transformations occurring across China's manufacturing sector.
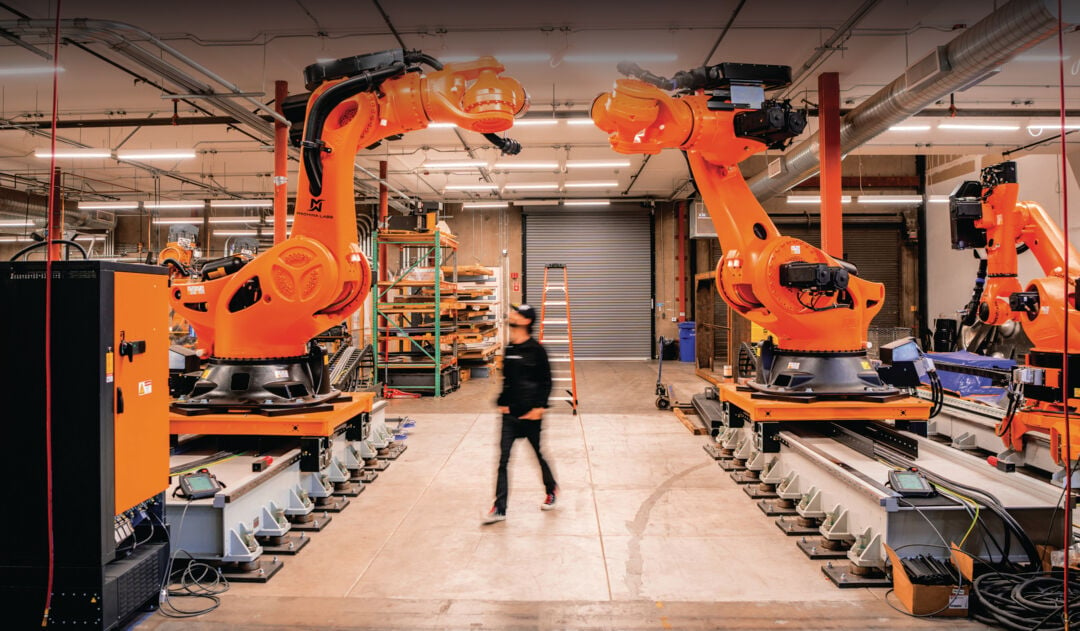

The social implications extend beyond employment patterns. Communities historically dependent on labor-intensive manufacturing face uncertain futures as automation becomes standard practice. Regional economic development strategies must now balance technological advancement with social stability considerations.
Some economists argue that ultra-automated manufacturing could eventually reduce China's competitive advantages based on labor costs, potentially redistributing global production as automation technology becomes more accessible internationally.
Investment Landscapes in Transition
The emergence of facilities like Xiaomi's creates distinct investment opportunities and risks across multiple sectors. Companies specializing in industrial robotics, particularly those supplying the 700+ robots operating in Beijing, may experience sustained demand growth as other manufacturers adopt similar approaches.
Battery manufacturers, including CATL and BYD FinDreams, which supply Xiaomi's various vehicle configurations, could benefit from the company's production scaling. However, investors should consider the cyclical nature of automotive manufacturing and potential overcapacity risks if EV demand growth moderates.

The gigacasting equipment sector, exemplified by companies like Haitian International and L.K. Technology, may experience increased demand as more manufacturers adopt simplified production methods. These suppliers could prove resilient even if individual EV manufacturers face challenges.
Conversely, traditional automotive suppliers focused on components that gigacasting eliminates may face structural headwinds. The consolidation of multiple parts into single cast components reduces demand for conventional assembly techniques and related equipment.
Technological Vulnerabilities and Systemic Risks
Ultra-automated production systems, while impressive in their efficiency, introduce new categories of operational risk. Single points of failure in software systems or robotic equipment can potentially halt entire production lines, creating vulnerability to cyber attacks or technical malfunctions.
Recent incidents, including a fatal accident involving a Xiaomi SU7 in April, have prompted increased regulatory scrutiny of advanced driver assistance systems and automated vehicle features. Such events could influence consumer acceptance and regulatory approval timelines for new technologies.

The complexity of maintaining 700+ robots operating in coordination requires specialized expertise that may be scarce as more facilities adopt similar approaches. This skills shortage could constrain expansion timelines and increase operational costs.
Future Trajectories and Market Evolution
Xiaomi's production capabilities position the company for potential expansion beyond China's borders, though current trade barriers necessitate careful market entry strategies. The company may pursue overseas assembly partnerships or direct investment in international manufacturing facilities to circumvent tariff barriers.
The success of ultra-automated EV production could accelerate similar investments by competing manufacturers, potentially creating manufacturing overcapacity if global EV demand fails to meet collective production capabilities. This scenario could trigger price competition that challenges industry profitability assumptions.
Table: Key Data on the Rapid Growth and Competitive Landscape of Electric Vehicle Models in China 2025
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| EV Market Penetration | >50% of all passenger vehicle sales were NEVs in H1 2025 (~5.4 million EVs out of 10.9 million) |
| BEV Share of NEVs | 61% of NEV sales |
| Top Selling Models | BYD Song, Geely Geome Xingyuan, Wuling HongGuang Mini EV, Tesla Model Y, BYD Seagull, Xiaomi SU7, Xpeng Mona M03 |
| Model Diversity | Multiple domestic and foreign brands competing with new launches monthly |
| Growth Rates | NEV sales +33% YoY in H1 2025; BEV sales +37.6% YoY |
| Market Share (June 2025) | Plugin vehicles 53%, BEVs 32% |
| Competitive Dynamics | EV average discounts ~10%; ICE discounts ~23%; significant price competition |
| Foreign Brand Strategy | Localized models for China market by Hyundai and others |
| Market Forecast | Plugin vehicle sales expected to exceed 10 million units in China by the end of 2025 |
Technological advancement in automated manufacturing may eventually democratize high-efficiency production, reducing China's current advantages in this domain. As automation technology becomes more accessible, geographic proximity to end markets may regain importance in manufacturing location decisions.
Recalibrating Automotive Reality
Xiaomi's 76-second production cycle represents more than manufacturing innovation—it signals the emergence of an entirely new paradigm for automotive production. As the global automotive industry grapples with electric transition, supply chain disruption, and geopolitical fragmentation, such facilities may become essential for competitive survival.

The implications extend beyond the automotive sector, suggesting broader transformations in how manufacturing industries approach automation, labor, and international competition. Whether Xiaomi's model proves economically sustainable at scale remains an open question, but its technological achievement has already altered perceptions of what automated manufacturing can accomplish.
For investors, policymakers, and industry participants, the Beijing facility serves as both inspiration and warning—demonstrating the potential for radical efficiency improvements while highlighting the disruptive consequences of technological transformation accelerated by geopolitical competition.
Investment Disclaimer: This analysis is based on current market data and established patterns. Past performance does not guarantee future results. Readers should consult qualified financial advisors before making investment decisions based on this information.