China’s Digital Canvas: How Alibaba’s Qwen-Image Is Changing the Game in AI Art
HANGZHOU, China — Alibaba’s Tongyi Qianwen team has introduced Qwen-Image, a powerful new model boasting 20 billion parameters. This open-source innovation not only rivals the performance of leading commercial systems but also showcases an exceptional grasp of Chinese visual language.
But this launch is more than just a technological breakthrough—it marks a strategic pivot in how major tech players approach AI accessibility. And with the global computer vision market projected at $12 billion, the implications for competition and investment are significant.

Open-Source with a Purpose
While many Western tech giants stick to closed, proprietary AI systems, Alibaba is taking a different route—openness. Qwen-Image is being released under the Apache 2.0 license, allowing for unrestricted commercial use. That decision comes at a time when regulatory scrutiny and geopolitical uncertainty are forcing companies worldwide to rethink how they handle intellectual property.
Quietly Revolutionary Technology
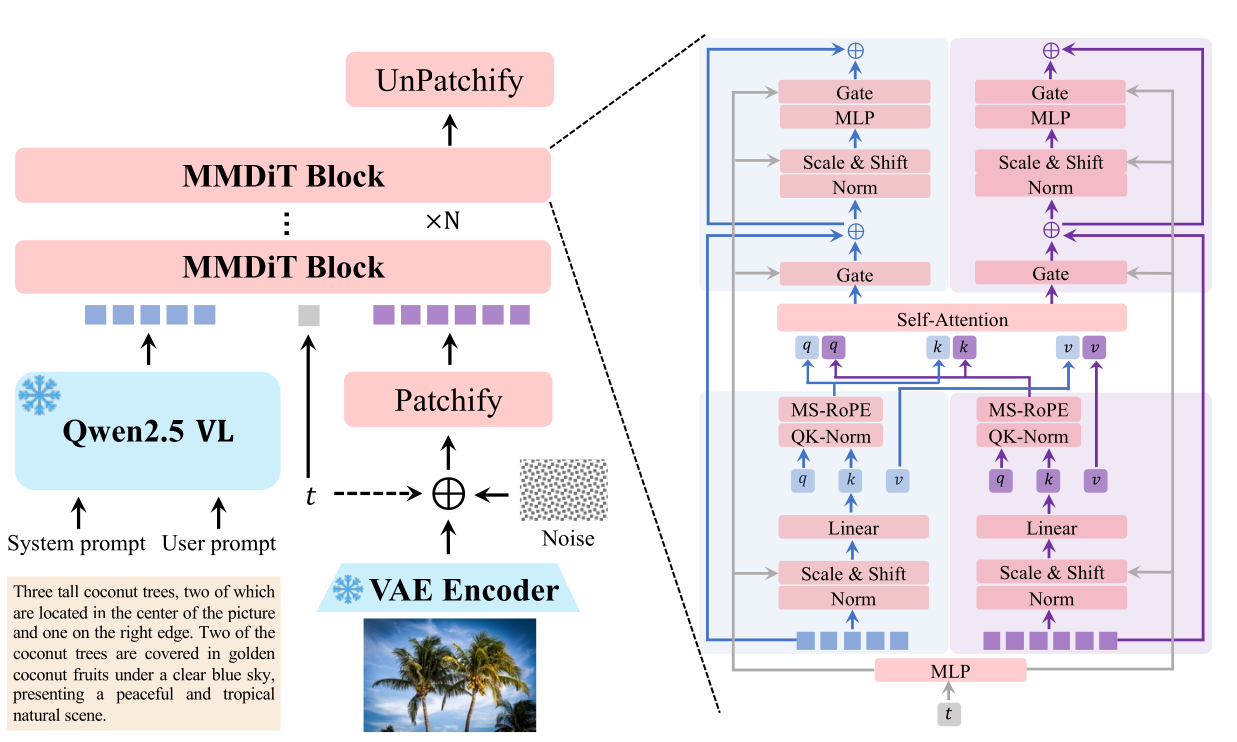
At the heart of Qwen-Image lies a sophisticated architecture designed to solve some of the biggest challenges in image generation. Its Multimodal Diffusion Transformer employs 60-layer transformer blocks and has been trained on more than a billion text-image pairs—a scale that puts it in direct competition with the largest closed-source models.
One standout capability is its handling of Chinese text, where Qwen-Image delivers what industry insiders are calling commercial-grade rendering quality. In benchmark tests, it has topped major evaluation frameworks like GenEval, DPG, and OneIG-Bench, and holds the highest open-source rating on Image Arena, with an Elo score above 1100.
“This isn’t just about printing characters into images,” one researcher noted. “It’s about deeply understanding visual language in context—a real paradigm shift.”
Making Advanced AI Widely Accessible
Perhaps Qwen-Image’s most disruptive feature is how accessible it is. Thanks to DFloat11 quantization and CPU offloading, the model can run on consumer-grade hardware—specifically, a single NVIDIA 3090 GPU. That opens the door for individual developers and smaller organizations to work with technology that previously required enterprise-level resources.
This could have major ripple effects. Many commercial AI platforms rely on high compute costs and subscription models to stay competitive. But Qwen-Image challenges that by offering a capabilities-first ecosystem, not a paywall.
Real-world testing shows just how versatile the model is—excelling in use cases from luxury product marketing to government documentation, and producing high-quality results across 18 scenarios, including bilingual travel guides and official paperwork needing precise formatting.
Smarter Multimodal Understanding
Qwen-Image isn’t just about creating beautiful images. Its architecture reflects a deeper strategy aimed at future-proofing AI systems.
Central to this is its MSRoPE (Multimodal Scalable RoPE) encoding method, which helps the model differentiate between text and images during processing. This advance boosts performance not only in image generation but also in visual tasks like object detection, depth estimation, and semantic segmentation.
Behind the scenes, Alibaba used a seven-stage data filtering pipeline to ensure high-quality alignment with human preferences, even at massive data scales. Add in techniques like Direct Preference Optimization and Group Relative Policy Optimization, and it’s clear the team prioritized alignment, precision, and learning efficiency.
Open Source as Strategy in a Geopolitical Context
The decision to open-source Qwen-Image isn’t just about tech. It’s a strategic geopolitical play.
With export controls and technology transfer restrictions tightening globally, open-source projects like this offer an alternative way to share innovation internationally. As Western scrutiny of Chinese tech intensifies, Alibaba’s transparent release could serve two purposes: proving its technological leadership and building goodwill within the global developer community.
Analysts believe this could pressure Western companies to re-evaluate their own IP strategies—especially in emerging markets where open-source solutions are gaining institutional support.
What This Means for Investors
For investors watching the AI space, Qwen-Image represents more than a flashy new product—it hints at shifting market dynamics.
By lowering barriers to entry, it could accelerate AI adoption in underserved segments, expanding the total addressable market while squeezing margins for premium service providers. Companies offering AI-as-a-Service may need to pivot toward specialized, value-added features to stay competitive.
On the other hand, hardware and cloud infrastructure providers stand to gain. With Qwen-Image proving that mid-tier GPUs can support powerful AI workloads, demand may rise for edge computing and distributed AI systems.
Those with exposure to semiconductors should take note: Alibaba’s efficiency-focused design may influence future GPU demand patterns, favoring flexibility over brute-force power.
A New Era of AI Competition
Qwen-Image may be the first open-source model to truly match commercial AI systems—especially when it comes to generating Chinese-language content. That milestone could accelerate the timeline for open-source dominance in other areas as well.
Its support for object editing, style transfer, and pose manipulation positions it to compete with—and possibly disrupt—traditional creative software markets. As these AI tools become standard in design workflows, established software vendors may face growing pressure from AI-native alternatives.
If Alibaba’s move sparks a wave of similar releases from other tech giants, we could see a shift from competing on basic capabilities to competing on integration and specialization.
Investors may need to rethink how they evaluate AI-driven companies. The value may move away from raw model performance and toward how well those models are embedded into real-world industry solutions.
While past success in AI development doesn’t guarantee future market leadership, the rise of open-source foundation models is a trend that can’t be ignored. Investors should speak with financial advisors to reassess their AI exposure in light of this rapidly evolving landscape.
