
Via Transportation Files for IPO as Transit Tech Company Eyes NYSE Listing
The Digital Transit Revolution Takes Wall Street: Via Transportation's Bold Public Debut
NEW YORK — Via Transportation, the decade-old startup that has been methodically rewiring how millions navigate their daily commutes, officially submitted its initial public offering documents to the Securities and Exchange Commission.
The timing is deliberate. As cities worldwide grapple with post-pandemic mobility patterns that have fundamentally altered the transportation landscape, Via's IPO represents more than a financial milestone—it signals the maturation of an industry where artificial intelligence meets public infrastructure, where municipal budgets intersect with cutting-edge technology.
For the 689 customers across 30 countries who depend on Via's unified transit platform, this moment represents validation of a radical premise: that the fragmented, siloed systems governing public transportation can be seamlessly integrated into a single, intelligent network.
When Silicon Valley Meets Main Street Transit
Via's journey to Wall Street began in 2012, when founder Daniel Ramot envisioned replacing the patchwork of disconnected transit technologies that plagued municipal transportation agencies. The company's core proposition—a cloud-based platform that unifies trip planning, real-time dispatch, eligibility verification, and fare payment—emerged from a simple observation: public transit agencies were drowning in vendor complexity.
"The fundamental challenge wasn't technological innovation for its own sake," explained one industry analyst familiar with Via's development. "It was about creating operational coherence in systems that had been cobbled together over decades by dozens of different vendors."
The numbers underscore this transformation. Via's revenue surged to $205.8 million in the first half of 2025, representing a 27% increase from the same period in 2024. Annual revenue reached $337.6 million in 2024, more than tripling from $100 million in 2021. Yet perhaps more telling is the narrowing of losses—from $50.4 million in the first half of 2024 to $37.5 million in the corresponding period of 2025, suggesting the company is approaching the elusive profitability that public markets increasingly demand.
Via Transportation's revenue growth and narrowing net losses from 2021 to H1 2025.
| Year | Revenue | Net Loss |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | $100.0 million | N/A |
| 2024 | $337.6 million | $90.6 million |
| H1 2024 | $162.6 million | $50.4 million |
| H1 2025 | $205.8 million | $37.5 million |
The $82 Billion Question: Market Size and Opportunity
Via's IPO filing reveals a market opportunity that extends far beyond traditional public transportation. The company estimates its serviceable addressable market at $82 billion across North America and Western Europe, expanding to $250 billion when including broader ticketing and payment systems. Globally, the public transportation market reaches $545 billion, with projected annual growth of 5% over the next five years.
A breakdown of Via's Total Addressable Market (TAM), showing the serviceable, expanded, and global market sizes.
| Market Segment | Region/Scope | 2023 Market Size (USD) | 2024 Market Size (USD) | Projected Market Size (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Transportation | Global | $223.88 Billion | $248.13 - $261.5 Billion | $409.00 Billion by 2033 |
| Public Transportation | North America | $29.65 Billion | - | $47.59 Billion by 2030 |
| Public Transportation | Western Europe | $59.84 Billion | - | $98.70 Billion by 2030 |
| Transportation Ticketing Systems | Global | $10.2 Billion | $12.36 - $15.91 Billion | $33 Billion by 2032 |
These figures reflect more than optimistic projections—they represent a fundamental shift in how transportation infrastructure is conceived and deployed. The traditional model of fixed routes and predetermined schedules is giving way to dynamic, data-driven systems that respond in real-time to demand patterns and operational constraints.
"What Via has accomplished is the creation of an operating system for public transportation," noted one municipal technology expert who requested anonymity. "Instead of managing separate systems for scheduling, dispatch, and payment, agencies can now orchestrate their entire operation through a single interface."
The Intelligence Layer: AI Meets Municipal Operations
The recent launch of "Via Intelligence," the company's artificial intelligence platform for public transit, represents perhaps the most significant evolution in Via's value proposition. This AI-driven system offers tools for scheduling optimization, predictive runtime analysis, and ridership modeling—capabilities that promise to transform how transit agencies allocate resources and respond to changing demand patterns.
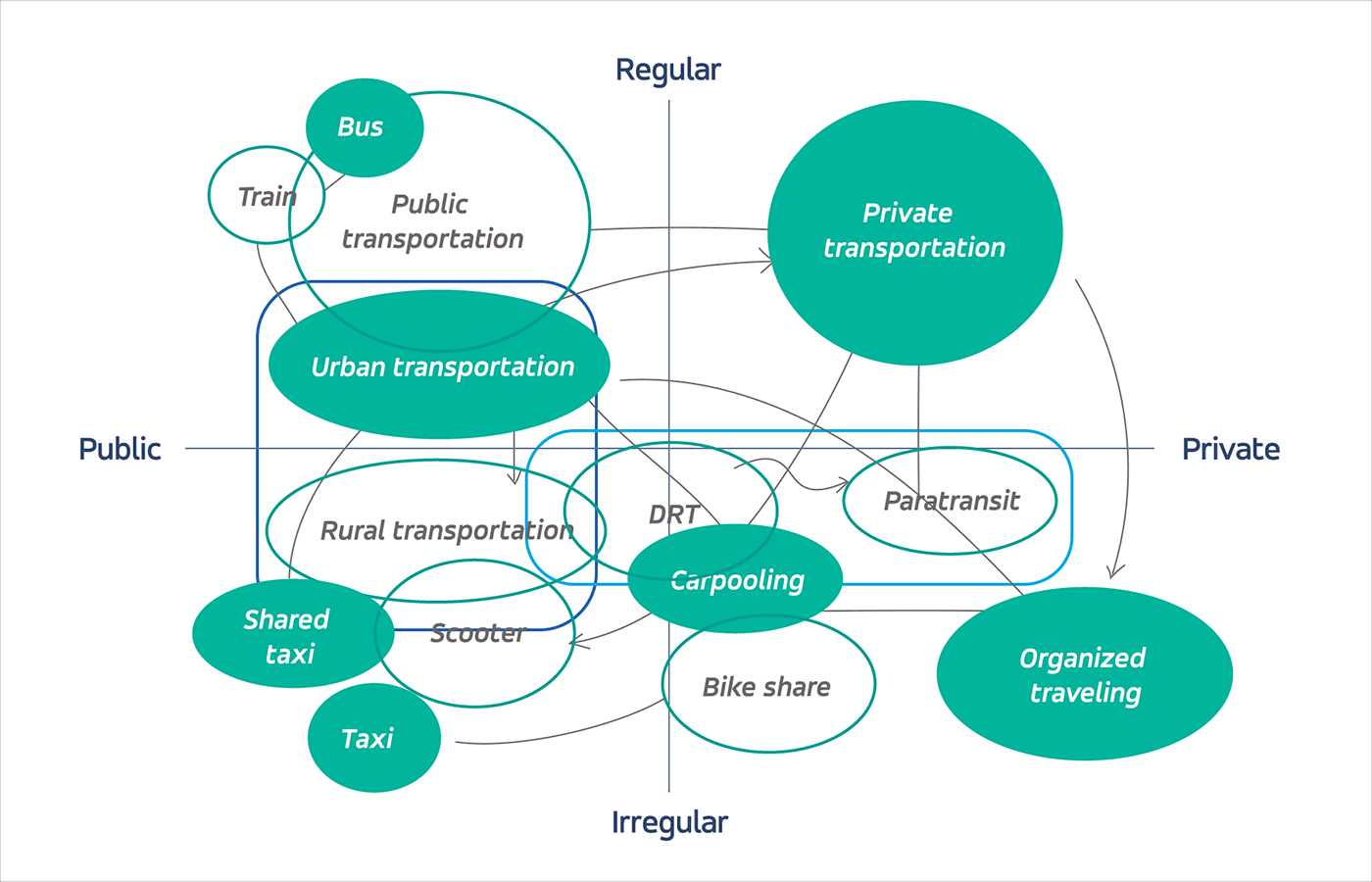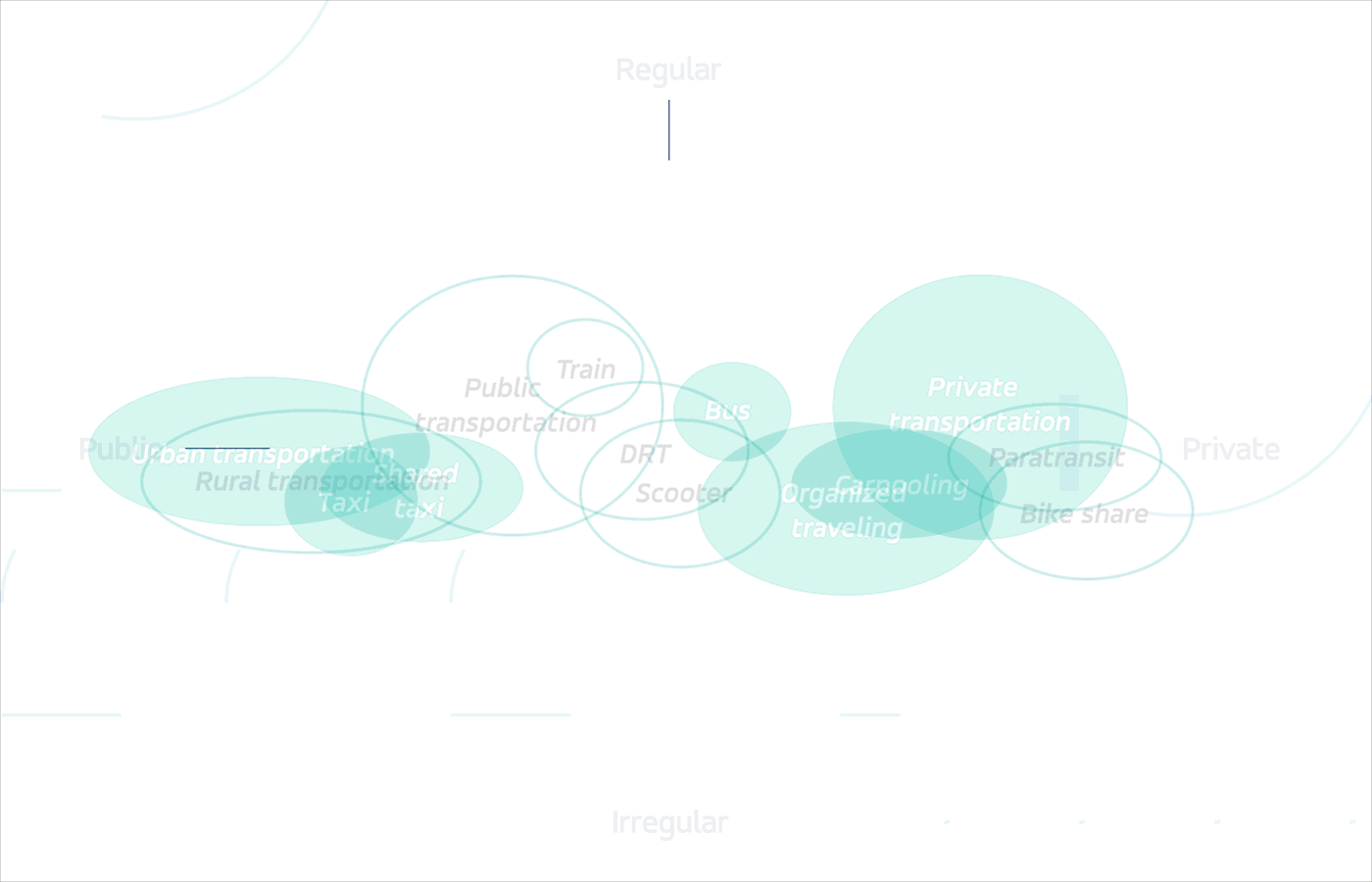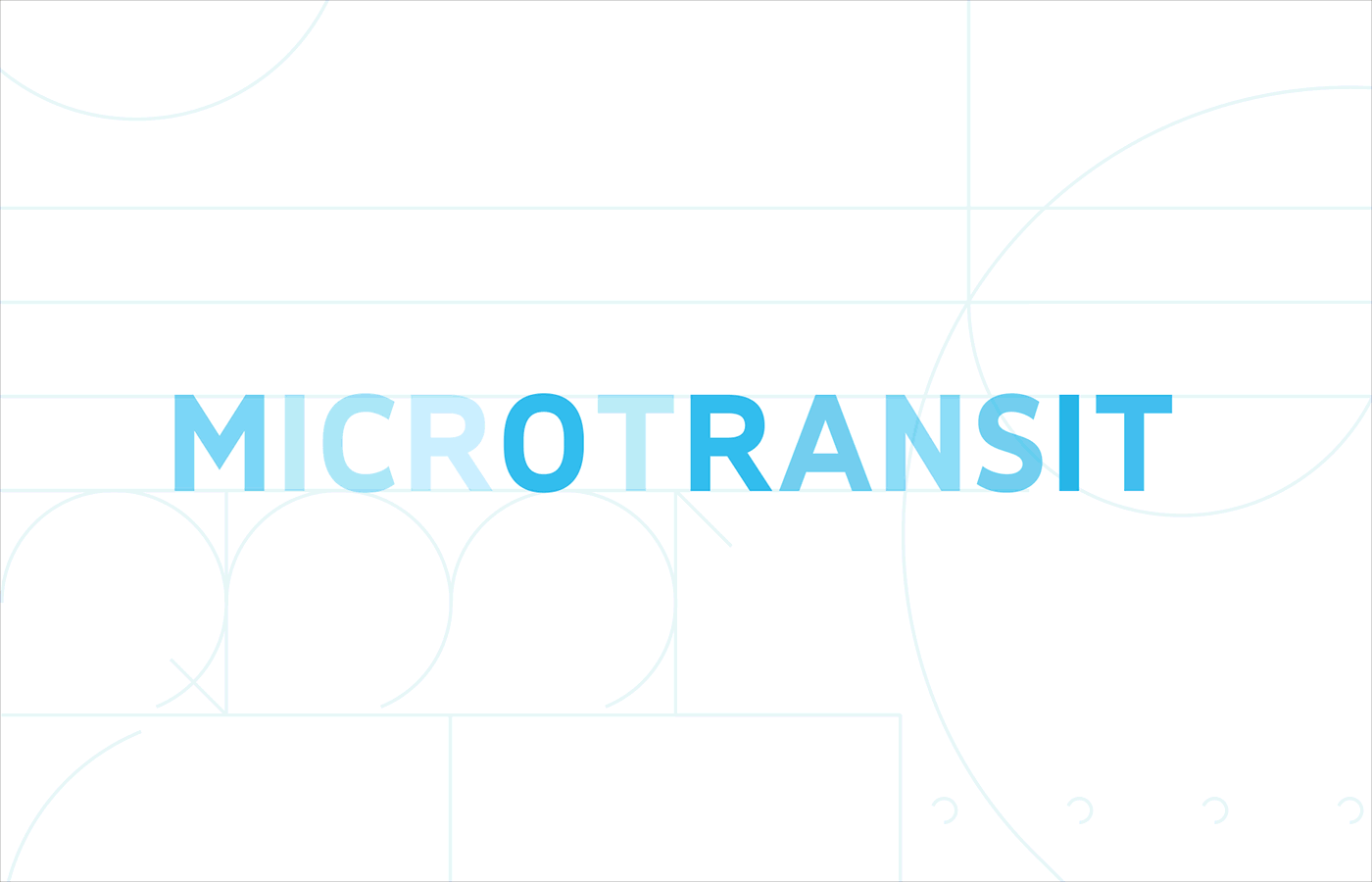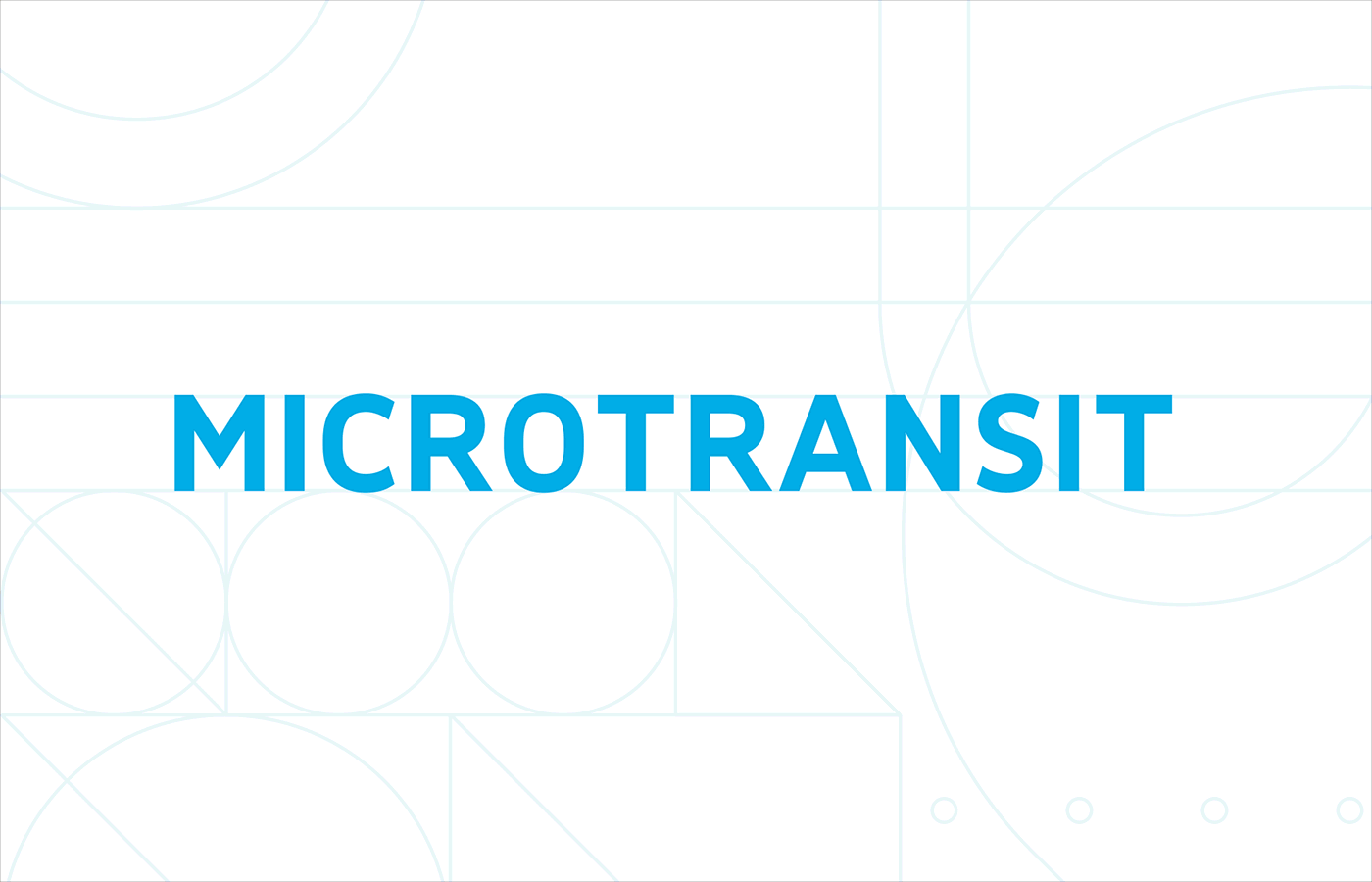
Microtransit is a flexible, on-demand public transit service that groups passengers heading in the same direction into a shared vehicle. It operates without a fixed schedule or route, instead using technology and "virtual bus stops" to create efficient, corner-to-corner journeys based on real-time rider demand.
The Denton County Transit Authority in the Dallas suburbs exemplifies this transformation. Using Via's microtransit planning tools, the agency achieved a five-fold increase in monthly ridership without expanding its budget—a testament to the efficiency gains possible through intelligent route optimization and demand forecasting.
Such achievements are particularly relevant as municipal budgets face increasing pressure. Transit agencies, long constrained by fixed costs and unpredictable ridership patterns, are discovering that artificial intelligence can deliver measurable operational improvements while maintaining service quality.
Financial Architecture and Market Positioning
Via's business model reflects the sticky, recurring revenue characteristics that public markets increasingly value. Approximately 95% of the company's revenue stems from multi-year subscription contracts, with usage-based components tied to fleet size and operational volume. This structure generates gross margins around 40%—lower than pure software companies due to the tech-enabled services component, but significantly higher than traditional transportation operators.
The company's customer retention metrics tell a compelling story of market validation. Gross retention exceeds 95%, while net revenue retention surpasses 120%—figures that indicate not only customer satisfaction but ongoing expansion within existing relationships. Average new contracts span 2.3 years, providing revenue visibility that municipal agencies value and investors appreciate.
Net Revenue Retention (NRR) is a key SaaS metric that measures the percentage of recurring revenue retained from existing customers over a specific period. The calculation accounts for revenue expansion from upgrades or cross-sells while also subtracting revenue churn from downgrades and cancellations. A high NRR indicates strong customer satisfaction and a company's ability to generate sustainable growth from its current customer base.
With $305.7 million in remaining performance obligations, 42% of which is expected to be recognized in the remainder of 2025, Via enters the public markets with substantial revenue backlog—a crucial indicator of business sustainability in an environment where growth-at-any-cost models have fallen from favor.
The Competitive Landscape: Integration Versus Specialization
Via's path to market leadership has required navigating a complex competitive environment populated by specialized players and entrenched legacy systems. Companies like Trapeze and Vontas dominate traditional paratransit and fixed-route scheduling, while newer entrants like Masabi lead in fare-as-a-service offerings.
The company's competitive advantage lies not in superior performance within any single function, but in the integration of multiple capabilities within a unified platform. This approach addresses a fundamental pain point for municipal procurement officers who must otherwise coordinate between numerous vendors while ensuring system interoperability.
Recent legal victories have reinforced Via's market position. In January 2025, the company prevailed in a patent infringement case against competitor RideCo, with a jury upholding Via's claims related to "virtual bus stop" technology—a key component of microtransit operations.
Investment Considerations: Growth Versus Profitability
Via's IPO occurs at a moment when public markets are reassessing the traditional growth-over-profitability paradigm that characterized much of the previous decade's technology investing. The company's path to profitability, while not yet achieved, appears increasingly clear as operational leverage emerges from its scaling subscription base.
Analysts suggest that Via's valuation may range between 4.5 to 5.5 times expected 2025 revenue, reflecting both the company's growth trajectory and the margin constraints inherent in its business model. This valuation framework positions Via below the multiples commanded by pure software companies while recognizing the recurring revenue characteristics and market opportunity that differentiate it from traditional transportation operators.
The dual-class share structure, with CEO Daniel Ramot retaining majority voting control through Class B shares, may limit takeover premiums but could provide operational continuity as the company navigates public market expectations while pursuing long-term strategic objectives.
A dual-class share structure is a system where a company issues at least two classes of stock with unequal voting rights. This structure allows a select group, typically founders, to maintain control through "super-voting" shares, even if they don't hold a majority of the company's equity.
Looking Forward: The Infrastructure Modernization Wave
Via's public debut coincides with a broader infrastructure modernization movement across developed economies. Federal and state funding programs increasingly prioritize technology-enabled efficiency improvements over traditional capacity expansion—a shift that favors companies capable of delivering measurable operational improvements within existing budgetary constraints.
The company's expansion strategy, funded in part by IPO proceeds, targets deeper penetration in European markets while accelerating sales and marketing efforts in North America. With 70% of current revenue concentrated in North America, successful international expansion could significantly broaden the company's addressable market while reducing geographic concentration risk.

As September's anticipated busy IPO calendar approaches, Via Transportation's public offering will test investor appetite for technology companies that operate at the intersection of public sector needs and private sector innovation. For municipalities worldwide struggling to modernize aging transportation infrastructure within constrained budgets, Via's market debut represents both validation of integrated technology solutions and a harbinger of the data-driven transit systems that may define urban mobility in the decades ahead.
The success of this offering may ultimately depend not on the sophistication of Via's technology platform, but on its ability to demonstrate sustained value creation for the public agencies that form the backbone of its customer base—a reminder that even in an era of artificial intelligence and cloud computing, the most transformative technologies are those that solve fundamental human problems with measurable efficiency and reliability.
NOT INVESTMENT THESIS